Sugar based polyols belong to the same digestible sugar group as sucrose and starch syrup, but offer a number of advantages, including better resistance to heat, acidity and alkalinity and lower assimilation. Sugar based polyols are widely used in products of used in foods, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. They also occur naturally in many items, including familiar fruits.
Characteristics of sugar based polyols
Sugar based polyols are widely used in processed foods as sweeteners with excellent physical, chemical, and physiological properties.
Sugar based polyols are low-calorie sweeteners and are used to improve the shelf life and anti-browning properties of food products.
They are also used in a wide range of other products, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals.
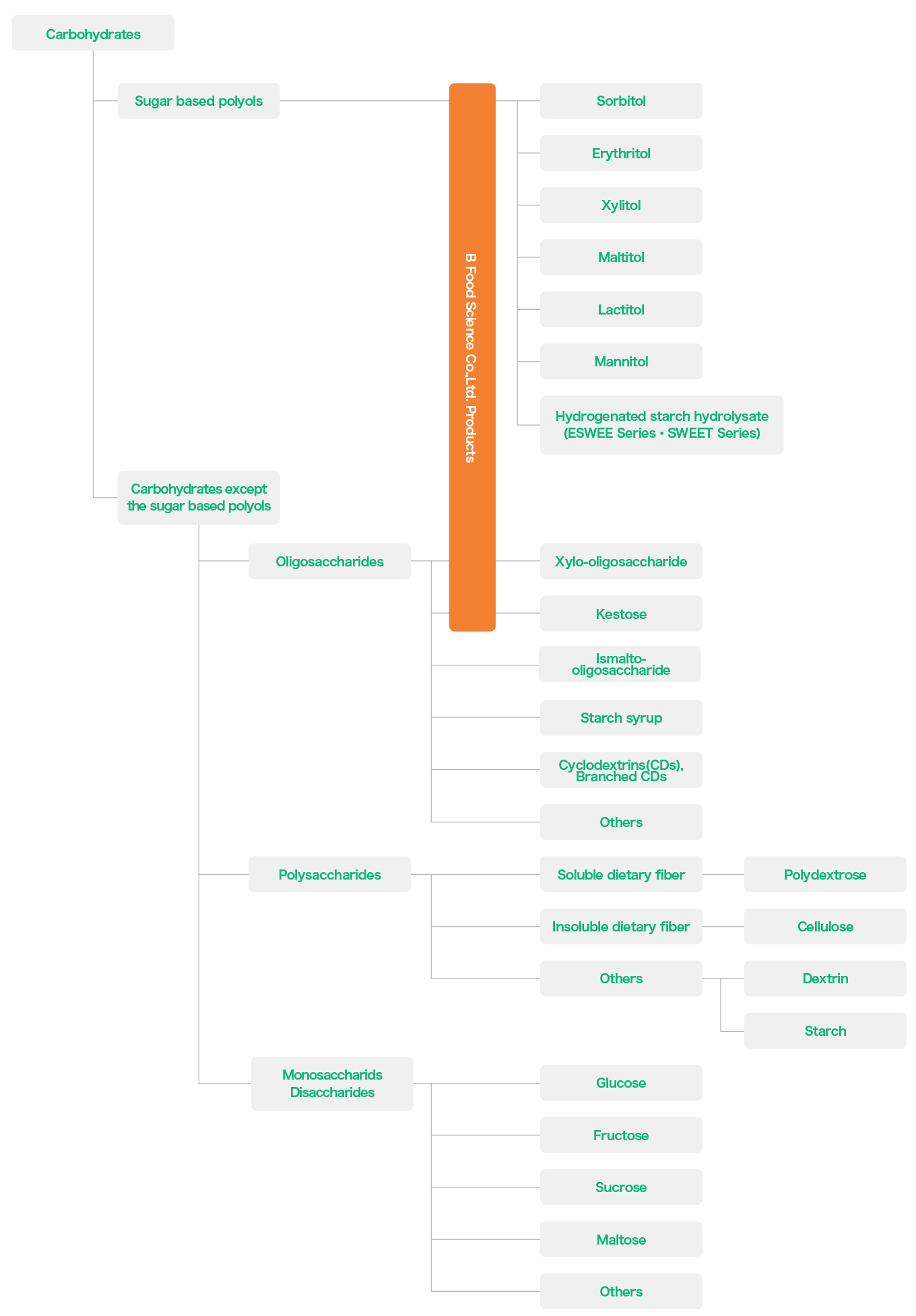
Positioning of sugar based polyols in carbohydrates
Three good points of sugar based polyols
-
1Low calories
Sugar based polyols are not readily hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes and resist absorption. For this reason, they have less calories than sucrose or glucose. Moreover, they do not affect blood sugar or insulin levels.
-
2Lower assimilation
Because Sugar based polyols are a poor nutrient source for microorganisms, they suppress the growth of microorganisms and help to extend product shelf life. They are also non-cariogenic.
-
3Non colorability
Because of their high resistance to heat, sugar based polyols will not exhibit browning when heated and will not trigger the Maillard reaction, which is a browning reaction between amino acids and digestible sugars. This characteristic reduces browning in processed foods.
Heat-induced browning
Because of their characteristic physical and chemical stability, sugar based polyols will not cause heat-related browning or trigger the Maillard reaction between amino acids and proteins.
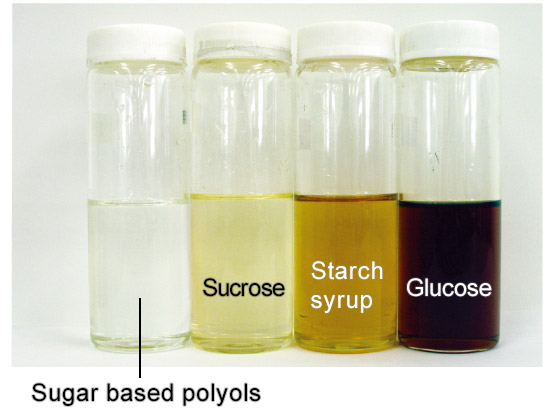

【Thermal condition】100℃ 6hrs / amino acid (glycine) 1% addition
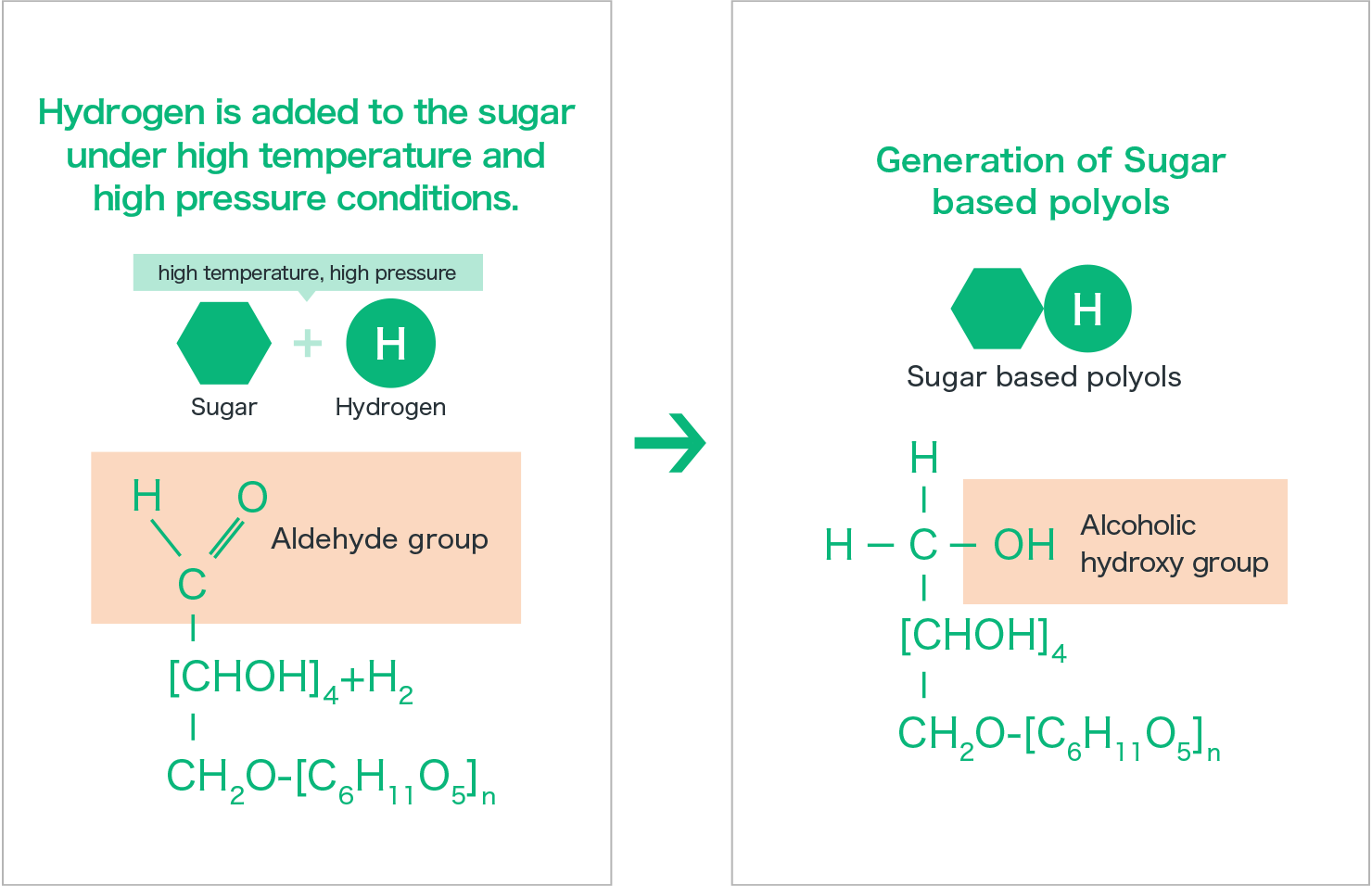
Production of sugar based polyols
Sugar based polyols are produced through the reduction (hydrogenation) of raw sugar.
Some sugar based polyols are also produced through bacterial fermentation.
Sugar based polyols are also found in familiar fruits.
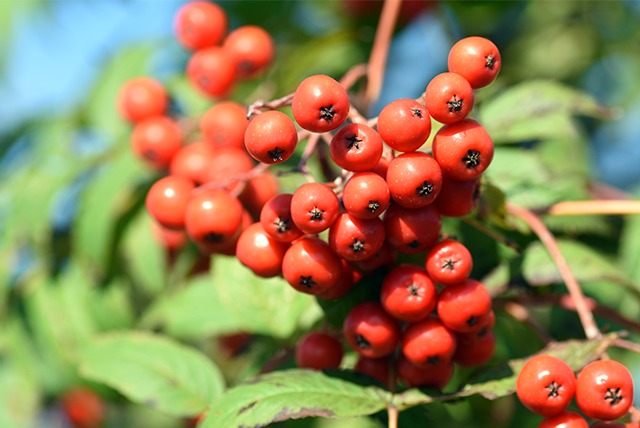

Sorbitol
The word “Sorbitol” is derived from sorbus aucuparia L., which is the botanical name of rowan, a member of the rose family. The fruit of the rowan contains sorbitol.
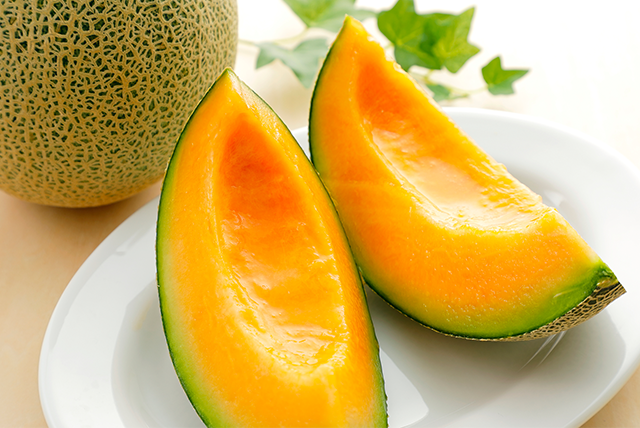

Erythritol
Erythritol is found in melons, pears and other fruits, in mushrooms, and in fermented foodstuffs such as miso and wine.
Sugar based polyols are used in many familiar products.
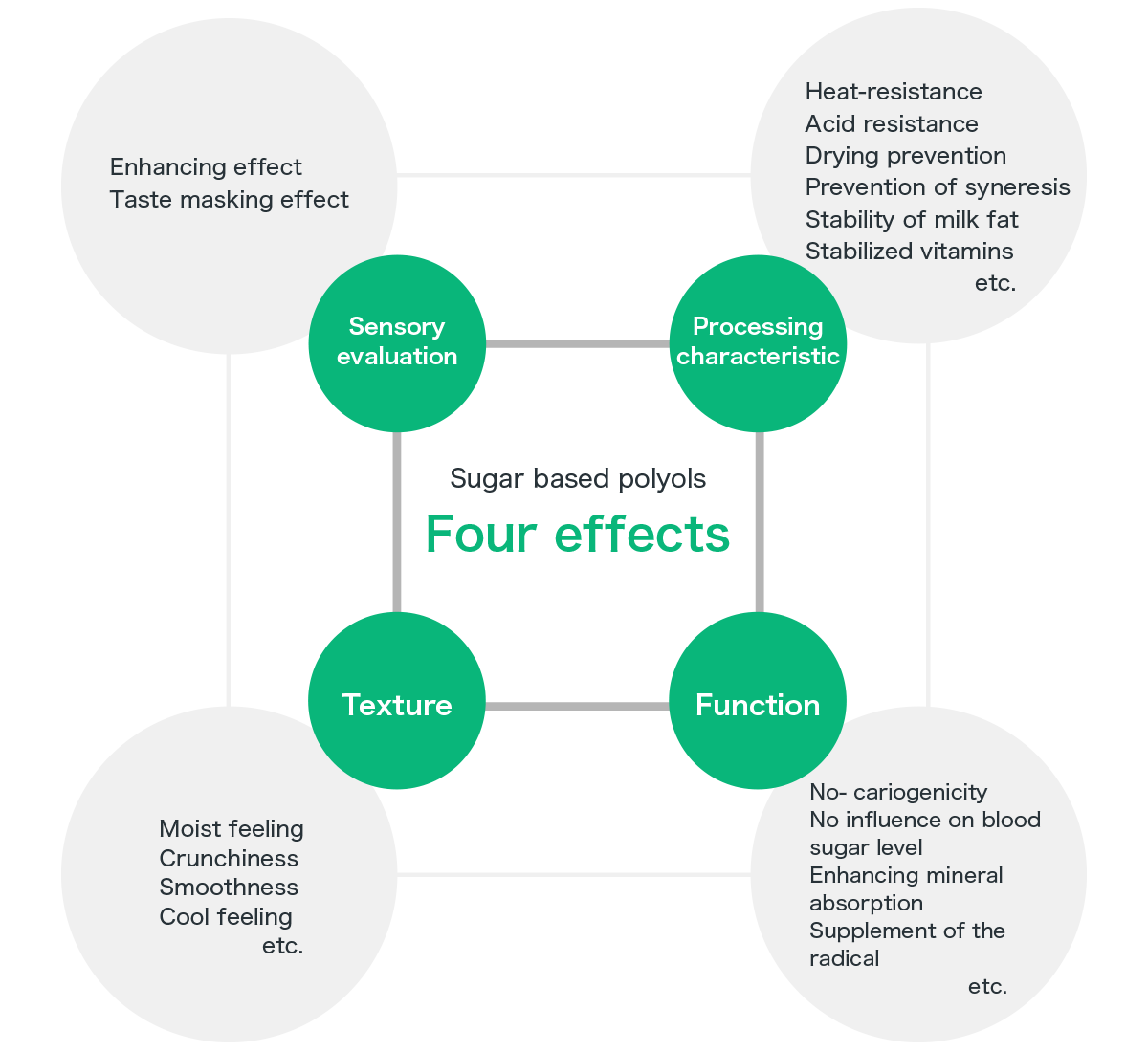
Effect of the sugar based polyols
About the laxative effect of sugar based polyols
Intake of a large amount of indigestible sugars, such as sugar based polyols, at one time may cause a temporary laxative effect. This is considered to occur because the sugar based polyols, which cannot be digested and absorbed in the small intestine, move to the colon, causing a rise in osmotic pressure. This is a temporary effect and is similar to the loosening effect that occurs when lactose intolerant people drink milk.
